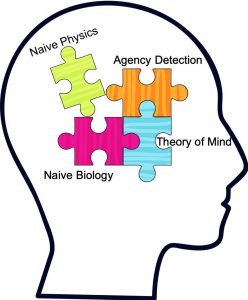
Barrett next raises what he sees as “reflective problems for atheists“. (For Barrett’s meaning of the term “reflective beliefs” see the opening post in this series: Gods (An Anthropology of Religion Perspective) and its specific application to belief/nonbelief in God, Argument for God — part 1.)
Barrett next raises what he sees as “reflective problems for atheists“. (For Barrett’s meaning of the term “reflective beliefs” see the opening post in this series: Gods (An Anthropology of Religion Perspective) and its specific application to belief/nonbelief in God, Argument for God — part 1.)
Barrett appears to be suggesting that an atheist must in some sense fight against his or her nature in order not to believe in god/s:
In addition to reinterpreting nonreflective beliefs that suggest superhuman agency, atheism requires combating conscious, reflective arguments for theistic thought. In some ways, the burden for certainty is greater for atheists than for theists. (111)
That last sentence is also problematic. “Burden for certainty”? But let’s continue.
Barrett quite rightly points out that the thrust of his explanations for why people believe in god/s or the supernatural of some kind indicates that belief is fundamentally easy. It would hardly be an explanation for the universal belief in the supernatural otherwise, though, would it! People do not need to “work hard” to figure out reasons why they believe. But then,
Given the sort of experiences they have, including the suggestion from others that God does exist, belief enjoys such rich intuitive support that no justification seems necessary. (Perhaps this is why some believers are such easy marks for those college professors that are hell-bent on dissuading them of their faith. They have few if any explicit reasons they can articulate for belief.) Atheism, on the other hand, has less in terms of intuitive support but brings more explicit rationale to the table. As a more reflective belief system, frequently intellectually discovered, atheism has more reflective opportunity for being challenged (as well as encouraged). Hence, explicit reasons for theism generally require some attention from the atheist. (111 – my bolded highlighting)
I can agree with all of that; I can even agree with those “college professors that are hell-bent” on demanding intellectual rigour from their students. In my journey out of belief, the last bastion I was left to face was my conviction that the Bible was “true” in some theological sense. Yes, I needed to address the explicit reasons for that belief just as I had had to address the explicit reasons for each other grounds for belief up till that point.
Reasons believers typically advance for their conviction that God exists are the need for agency to explain the existence of the universe and design in the world around us. Until the arrival of “Darwinism”, Barrett notes, atheists had no real “satisfying defense against their own intuitive sense that the world was designed and the congruent claims of theists.” That may be so. But I am reminded of a time when thunder was universally believed to be the noise of divine or spirit activity of some sort, according to some of our ancient records. And how for a long time planets strangely wandered in their idiosyncratic pattern — as if (how else?) moved by some divine or spirit agent.
Meanwhile, Barrett points out that Darwinism does not address “the origin of life or the mechanical fine-tuning that many astronomers and physicists have recently noted… (Leslie 1982, Leslie 1983, Carter 2002)”. Yes. There is still more to learn. Explaining thunder was but one of the first steps.
Then Barrett returns to his concern for “certitude”:
Atheists may also have epistemological difficulties that theists (depending on theology) do not have. Theists may confidently hold reflective beliefs operating under the assumption that their mind was designed by an intelligent being to provide truth, at least in many domains. For the atheist, another explanation for the certitude of beliefs must be found, or certitude must be abandoned. If our very existence is a cosmological accident and our minds have been shaped by a series of random mutations whittled by survival pressures (not necessarily demanding truth, only survival and reproduction, as a rat, fly, or bacteria can pull off with their “minds”), then why should we feel confident in any belief? And if we can’t feel confident in our beliefs, why do we go through life pretending we can? These questions may have satisfactory answers. The point is that unlike the theist, the atheist has far more explaining to do. This, too, makes atheism harder. (112 — again, my bolding)
I certainly have no problem accepting that our brains have not evolved in such a way that will enable them to grasp a complete understanding of everything we would like. I know quantum physics and even advanced maths are beyond my abilities to comprehend fully. I am quite prepared to accept that the noises I hear my old wooden house at night are the result of contraction from temperature drops, but I am not going to launch a crusade if one day we discover some other mechanism for the noises. In other words, all “certitude” is provisional — we are always open to learning more, revising the old, even discarding it, and moving on. That kind of provisionality as the bedrock is what has enabled us to survive at all, I suspect — not any unqualified or unquestionable “certitude”.
Returning to thunder. Yes, a naturalist has much more explaining to do than the person who attributes the noise to Hephaestus or Zeus or some other divine activity. Why should that be a problem? A child can readily imagine a monster at night; it takes some “reflective activity” to think of plumbing and other noises as the temperature drops. Not every rustle in the grass is caused by a stalking tiger.
Fighting Back Theism
“Fighting Back Theism” is a heading chosen by Barrett. For me it conjures images of the rebellious, renegade atheist fighting wilfully and desperately against the God he “knows” (or “wishes not”) to exist yet also hates. For Barrett,
Atheism just requires some special conditions to help it struggle against theism.
Continue reading “Argument for God — part 3, final (arguments against atheism)”